-
19
Feb.
Improving the durability of irrigation equipment: the impact resistance of the metal impact sprinkler RT-9708E
In various agricultural production environments, irrigation equipment often faces the test of external impact, mechanical collision and bad weather. Whether it is mechanized operation in farmland operation or the impact of natural environment such as storm and...
-
12
Feb.
Rain Gun RT-9821B: Bringing efficient solutions to large-scale agricultural irrigation
Traditional irrigation equipment often requires a lot of manual operation and technical adjustment, and farmers often need to spend a lot of time and energy in the process of using it. The introduction of Rain Gun RT-9821B solves this problem. The device is de...
-
04
Feb.
Adapting to various farmland environments, Plastic Impact Sprinkler RT-9703C improves irrigation efficiency
Large-scale farmland irrigation often faces challenges such as wide coverage area, large irrigation water volume, and complex land morphology. Although traditional sprinkler systems can cover a certain range, they usually have problems such as uneven spraying,...
-
26
Jan.
Innovative atomizing nozzles help efficient agricultural irrigation, On Line Refraction Mist Nozzle RT-DMZS085B improves water resource utilization
On Line Refraction Mist Nozzle RT-DMZS085B uses a unique atomization technology that can convert water flow into extremely fine water mist. This atomization effect makes the water droplets extremely small, forming a uniform and fine spray, which can minimize w...

SINCE
2003
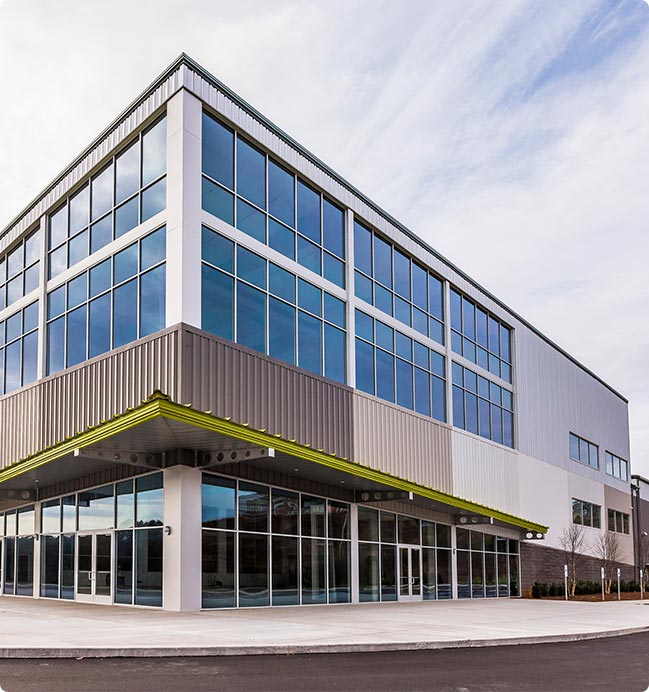
Welcome To Runte
View More
As a professional China Pipeline Connectors Manufacturers and Hose Reels Factory, Ningbo Runte Irrigation Equipment Co., Ltd. was founded in 2005. It is a modern enterprise focusing on the research, development, production, and sales of water-saving irrigation equipment and water purification equipment. We have a mold warehouse, more than 15 injection machines, and a test office. Our products gain great reputations from our clients in China and all over the world.
-
 18 years experience in landscape irrigation
18 years experience in landscape irrigation -
 A complete and reliable supply chain system
A complete and reliable supply chain system
Recent News
Industry Knowledge Expansion
Can pipeline connectors be used for both onshore and offshore applications?
Pipeline connectors can indeed be used for both onshore and offshore applications. These connectors play a crucial role in the efficient and safe transportation of fluids, such as oil, gas, and water, through pipelines. They are used to join pipeline sections, allowing for easy installation, maintenance, and repair work.
In onshore applications, pipeline connectors are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, water distribution, and wastewater management. These connectors enable the junction of various pipeline sections, ensuring a continuous flow of liquids. One of the main advantages of using pipeline connectors onshore is the ability to quickly connect and disconnect sections, reducing downtime during repairs or modifications. Onshore pipeline connectors are typically designed to withstand a wide range of pressures and temperatures, as well as external forces like soil movement or seismic activity.
Offshore applications, including subsea operations and offshore drilling platforms, also heavily rely on pipeline connectors. These connectors are specifically designed to withstand the extreme conditions found in offshore environments, such as high pressures, corrosive saltwater, and unpredictable weather. Offshore pipeline connectors are required to meet stringent safety and quality standards due to the consequences of any failure or leakage. They are often constructed with materials resistant to corrosion, such as stainless steel, and are equipped with sealing mechanisms that ensure a reliable and leak-free connection.
In both onshore and offshore applications, there are various types of pipeline connectors available that cater to different requirements. Flange connectors, for example, consist of two flanges that are bolted together, forming a sturdy connection. They are commonly used in larger diameter pipelines that require high strength and structural integrity. Another type is the mechanical coupling, which utilizes mechanical means (such as threaded or compression fittings) to join pipeline sections. These connectors are often used in smaller diameter pipelines and provide easy installation and disassembly.
Furthermore, advancements in pipeline connector technology have led to the development of specialized connectors for specific applications. For instance, offshore applications may require connectors with a high tolerance for lateral movement or equipment with ROV (remotely operated vehicle) operability for subsea installations. Additionally, there are connectors designed for pigging operations - a process in which cleaning devices or inspection tools are propelled through the pipeline.
How do pipeline connectors handle axial and lateral movements in a pipeline system?
Pipeline connectors are designed to handle both axial and lateral movements in a pipeline system. These movements can occur due to various factors, such as changes in temperature, soil settlement, seismic activities, or even intentional adjustments during installation.
Axial movement refers to the expansion or contraction of the pipeline due to temperature changes. This movement can be accommodated by using expansion joints or expansion loops in the pipeline system. Expansion joints are flexible connectors that can absorb axial movement by allowing the pipeline to expand or contract without causing stress or damage. They are typically made of materials like rubber or metal bellows that can withstand the pressure and temperature of the fluid being transported.
Lateral movement, on the other hand, refers to the horizontal displacement of the pipeline. This can occur due to soil settlement or seismic activities. To handle lateral movement, pipeline connectors often incorporate swivel or ball joints. Swivel joints provide rotational movement, allowing the pipeline to adjust to lateral displacements without putting stress on the connectors or causing pipeline failure. Ball joints, on the other hand, allow for both rotational and angular movement, providing flexibility in handling lateral displacements.
In addition to expansion joints and swivel/ball joints, pipeline connectors may also utilize other mechanisms to handle movements. These include slip joints, which are used to accommodate axial movement by allowing one section of the pipeline to slide over another, and flexible hose connections, which provide flexibility to absorb both axial and lateral movements.
It is important to note that the design and selection of pipeline connectors depend on various factors, including the magnitude of the movements, the pressure and temperature of the fluid, the diameter and length of the pipeline, and the specific requirements of the application. Engineers and pipeline designers must carefully analyze these factors to determine the appropriate type and configuration of pipeline connectors to ensure the integrity and safety of the pipeline system.
Pipeline connectors not only facilitate the efficient transportation of fluids through pipelines but also play a crucial role in accommodating movements and maintaining the structural integrity of the system. They are designed to handle axial and lateral movements, ensuring the uninterrupted flow of fluids and reducing the risk of leaks or failures in onshore and offshore pipeline applications.


 English
English Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体